Healthcare apps have emerged as powerful tools for doctors as well as patients, and tertiary healthcare providers like insurance, laboratories and more. They offer convenience and accessibility to patients while revolutionizing the way healthcare services are delivered. From monitoring vital signs to scheduling appointments, these apps have become integral to modern healthcare systems. However, amid this innovation, there’s a critical factor that app developers cannot afford to overlook: HIPAA compliance.
The healthcare industry has the highest cost of data breaches, with an average of $10.93 million in 2023, according to the World Economic Forum. This is almost double the cost of data breaches in the financial industry, which is second with an average of $5.9 million. This is the 13th year in a row that the healthcare industry has the highest cost of data breaches.
What is HIPAA?
HIPAA, the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act, sets the standard for protecting sensitive patient information in the United States. It is a United States legislation enacted to ensure the privacy and security of individuals’ protected health information (PHI) while also providing guidelines for the electronic transmission of healthcare data.Top of Form
For developers entering healthcare app development, understanding HIPAA regulations is not only essential but also legally mandated. Failure to comply can lead to severe consequences, including hefty fines and reputational damage. Therefore, before you begin developing a healthcare app, developers must grasp the fundamentals of HIPAA compliance to ensure both the integrity of their applications and the privacy of their users’ data.
If a healthcare app fails to adequately safeguard patients’ medical records, resulting in a data breach, the ramifications extend far beyond mere technical error. Such an incident constitutes a breach of trust, representing a fundamental violation of patient privacy and confidentiality. It also has the potential to trigger severe consequences, both for the affected individuals and the entities responsible for safeguarding their data. HIPAA was formulated to prevent just that.
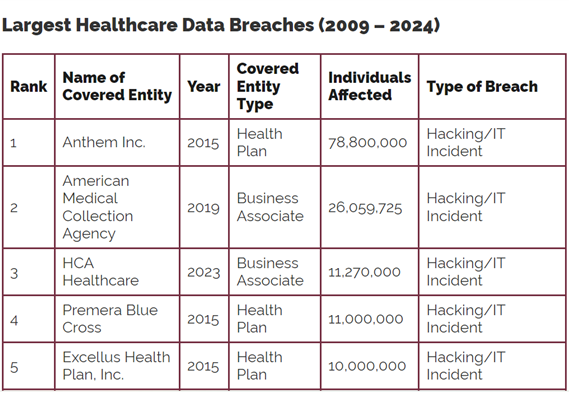
In 2015, the healthcare industry witnessed one of the largest data breaches in history when Anthem Inc., a leading health insurer, fell victim to a cyberattack compromising the records of nearly 80 million individuals. The fallout was staggering – reputational damage, legal battles, and untold financial repercussions.
Source: HIPAA Journal
But it’s not just the fear of cyberattacks that haunts the healthcare app landscape. Even inadvertent mishandling of patient data can lead to grave repercussions.
HIPAA compliance isn’t an afterthought. It’s the cornerstone upon which the entire edifice of healthcare technology stands.
When it comes to healthcare app development, ignorance isn’t bliss. Overlooking compliance is not merely an oversight—it’s a potential catastrophe waiting to unfold. The stakes are undeniably high, with real risks that demand meticulous attention, for in healthcare, the cost of ignorance is more than just money – it impacts lives.
Understanding the Basics of HIPAA
HIPAA, enacted in 1996, comprises several rules designed to protect patients’ health information. The Privacy Rule establishes standards for safeguarding PHI, ensuring its confidentiality and limiting its use and disclosure. The Security Rule sets forth requirements for securing electronic PHI (ePHI) and protecting it from unauthorized access, alteration, or destruction. Additionally, the Breach Notification Rule mandates covered entities to notify affected individuals, the Department of Health and Human Services (HHS), and, in some cases, the media, in the event of a breach compromising PHI.
HIPAA’s Significance in Healthcare
HIPAA’s significance in healthcare cannot be overstated. By imposing strict standards for PHI protection, it fosters trust between patients and healthcare providers, ensuring the confidentiality of sensitive medical information. Compliance with HIPAA not only mitigates the risk of data breaches and legal consequences but also upholds patients’ rights to privacy and control over their health data.
Implications of HIPAA Non-Compliance
Failure to comply with HIPAA regulations carries significant consequences. Organizations found in violation may face civil monetary penalties ranging from thousands to millions of dollars, depending on the severity of the breach and the organization’s level of culpability. Moreover, non-compliance can lead to reputational damage, loss of patient trust, and potential criminal charges for deliberate violations.
HIPAA Compliance for App Developers – Key Terms to Know
Familiarity with key terms and concepts that form the foundation of its regulations central to understanding HIPAA, for ensuring compliance and maintaining the privacy and security of individuals’ health information.
Protected Health Information (PHI)
PHI includes any individually identifiable health information transmitted or maintained by a covered entity or its business associate, such as medical records, test results, and billing information.
Covered Entities
Covered entities are individuals or organizations subject to HIPAA regulations, including healthcare providers, health plans, and healthcare clearinghouses.
Business Associates
Business associates are entities that perform functions or activities on behalf of a covered entity involving the use or disclosure of PHI, such as IT vendors or billing companies.
Minimum Necessary Standard
This standard requires covered entities to limit the use, disclosure, and request of PHI to the minimum amount necessary to accomplish the intended purpose.
Notice of Privacy Practices (NPP)
The NPP is a document that covered entities must provide to individuals, explaining their privacy rights and how their PHI may be used and disclosed.
Breach
A breach is an impermissible use or disclosure of PHI that compromises its security or privacy. Covered entities must assess breaches and notify affected individuals and regulatory authorities when necessary.
How to Make Your App HIPAA Compliant?
Unique User Identification: Implement a unique user identification system, such as usernames or account numbers, to ensure accountability for accessing and handling PHI.
Automatic Logout: Enforce automatic logout features to terminate user sessions after a period of inactivity, reducing the risk of unauthorized access to PHI.
Emergency Access Procedures: Develop and document emergency access procedures to allow authorized personnel to access PHI in urgent situations while maintaining security and confidentiality.
Encryption of ePHI: Encrypt electronic protected health information (ePHI) both at rest and in transit to protect it from unauthorized access or interception.
Protected Data Transfer Networks: Utilize secure data transfer protocols and networks, such as encrypted connections (e.g., HTTPS), to ensure the secure transmission of PHI between devices and servers.
Regular Information System Audits: Conduct regular audits of information systems and data access logs to monitor and track user activities, identify security incidents, and ensure compliance with HIPAA regulations.
Password Management: Implement strong password policies and mechanisms, including requirements for complex passwords, regular password updates, and restrictions on password reuse.
Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): Enable two-factor authentication (2FA) to add an extra layer of security by requiring users to verify their identity using a second authentication method, such as a one-time code sent to their mobile device.
Access Controls: Implement granular access controls to restrict access to PHI based on user roles and permissions, ensuring that only authorized individuals can view or modify sensitive information.
Data Backup and Recovery: Establish regular data backup procedures and disaster recovery plans to mitigate the risk of data loss or corruption, ensuring the availability and integrity of PHI in the event of a system failure or breach.
Employee Training and Awareness: Provide comprehensive HIPAA training to employees and contractors involved in app development and maintenance to ensure they understand their responsibilities and obligations regarding PHI security and privacy.
HIPAA Compliance Documentation: Maintain detailed documentation of HIPAA compliance efforts, including policies, procedures, risk assessments, and audit trails, to demonstrate adherence to regulatory requirements and facilitate compliance audits.
How to Get a HIPAA Compliance Certificate?
There is no HIPAA compliance certificate, or agency that provides one. Just follow the aforementioned guidelines to ensure you have the necessary safeguards in place to keep your app safe from data breaches and their dire consequences.
Conclusion
Navigating HIPAA compliance is a prerequisite for developers venturing into the healthcare app space. By understanding the intricacies of HIPAA regulations, implementing robust security measures, and fostering a culture of compliance, developers can build applications that prioritize patient privacy and safety. Collaboration with healthcare experts and staying updated with evolving regulations are essential for ensuring sustained compliance and success in the dynamic healthcare landscape.