The world of mobile apps in 2026 is no longer about chasing the latest buzz or copying what everyone else is doing. The market is crowded, users are more selective, and the cost of mistakes is higher than ever. App development trends for 2026 are about practical innovation, measurable impact, and long-term scalability. At Moveo, we focus on filtering the noise and identifying which trends genuinely deliver value and which are simply hype.
Mobile and app platforms remain a massive market, with research projecting the mobile application development market to grow significantly by 2031 (from around USD 243 billion in 2025 to nearly USD 546 billion in 2031). This reinforces how investment is still accelerating in tools and frameworks that power next‑gen apps.
1. On-Device Intelligence
Generative AI made headlines, but the next evolution in mobile apps is on-device AI. Instead of relying on cloud processing, apps are now able to handle complex AI functions locally on the device. This reduces latency, enables offline functionality, and improves user privacy.
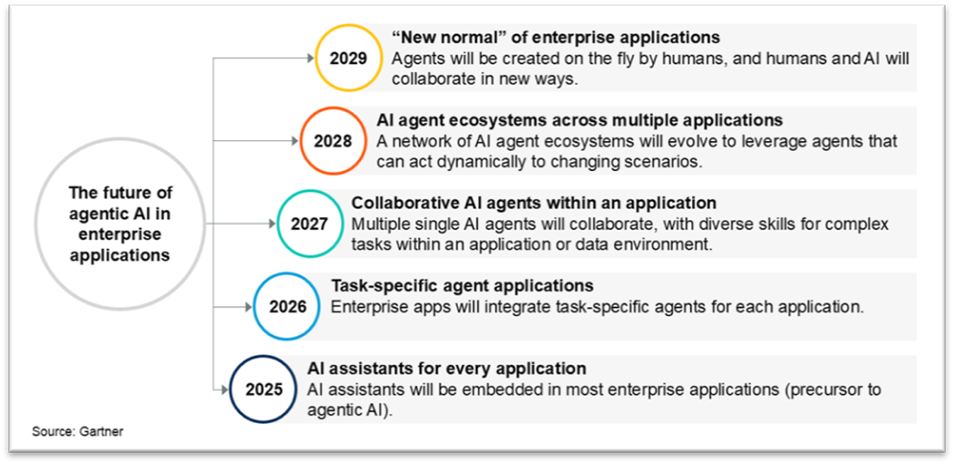
Gartner predicts that by the end of 2026, around 40 % of enterprise applications will feature task‑specific AI agents, up from very low adoption just a year prior, signaling a dramatic mainstreaming of intelligent features inside business apps.
On-device intelligence allows predictive keyboards to learn user behavior without sending personal data to the cloud, AR applications to render effects in real time, and recommendation engines to deliver faster, more relevant results. In 2026, apps that integrate AI locally rather than just using it as a flashy cloud service will set a new standard for speed, reliability, and trust.
Examples:
- A news app that learns reading habits and suggests stories instantly.
- Health trackers that predict trends in user activity without sending data externally.
2. Super-Apps and Micro-Experiences
The concept of a super-app, which bundles multiple services into a single platform, has been largely successful in Asia but elusive in the West. This is changing thanks to App Clips for iOS and Instant Apps for Android, which allow users to access micro-experiences without downloading the full app.
Startups can test new features, offer task-specific experiences, and reach more users with minimal friction. A payment feature, a booking system, or a small interactive tool can be delivered instantly, increasing adoption while keeping the core app lean. Super-app functionality is finally becoming practical, and apps that leverage micro-experiences will have a strategic advantage in 2026.
Example:
- A travel app offering an Instant App version for booking airport transfers. Users complete the transaction without installing the full app.
3. 5G-Native Apps
The rollout of 5G networks is transforming what mobile apps can do. Speed is only the surface benefit. The real potential lies in zero-latency cloud streaming, massive IoT integration, and real-time data processing.
Access to 5G is expanding rapidly, with 73 % of smartphone users reporting they now have 5G coverage, a clear jump over 2024 adoption levels. This underpins the case for 5G‑native apps and real‑time experiences.
Apps designed to be 5G-native can stream ultra-high-resolution video, power AR and VR experiences without lag, and manage connected devices seamlessly. For example, smart home or industrial IoT apps can collect and process data instantly, enabling decisions that were previously impossible.
Example:
- A fitness app streaming live group workouts in full AR with no lag.
- Industrial IoT apps collecting sensor data from multiple locations and issuing alerts instantly.
4. Privacy as a UX Feature
Compliance with GDPR and other regulations is no longer enough. In 2026, privacy-by-design will become a core user experience feature. This includes practices such as data masking, decentralized identifiers, and end-to-end encryption that are built into the workflow rather than added as an afterthought.
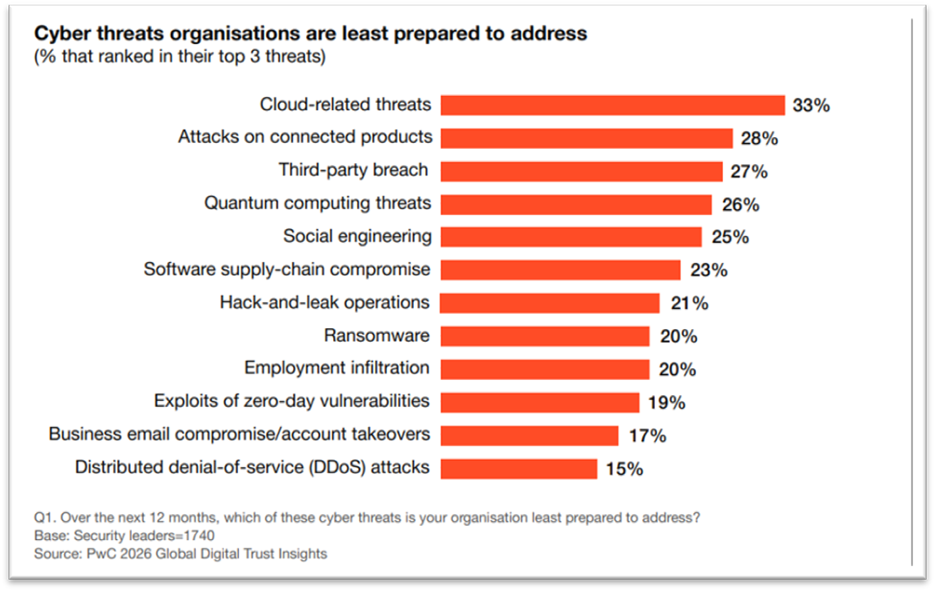
PwC’s 2026 Global Digital Trust Insights Survey of 3,887 executives shows that 60 % of organizations are increasing investment in cyber risk management in response to global uncertainty, a clear indicator that security and privacy must be core, not afterthoughts in app design.
Users are increasingly aware of how their data is used, and they respond positively to apps that make privacy transparent, intuitive, and seamless. Startups that treat privacy as a design principle rather than a legal checkbox will see higher retention, stronger engagement, and a measurable competitive advantage.
Examples:
- A messaging app that allows selective message expiry with one tap.
- A health app that anonymizes data while still providing personalized insights.
5. Cross-Platform Maturity
Cross-platform frameworks like Flutter and React Native have evolved to a point where they no longer represent compromises in performance or design. In 2026, they allow startups to build high-quality apps that function like fully native applications while maintaining a single codebase. This reduces development time, lowers costs, and makes iterative improvements faster.
For most startups, cross-platform development is not a second-choice strategy, but a deliberate decision that balances speed, scalability, and resource efficiency.
Apps built on these frameworks can reach both iOS and Android users without sacrificing quality, and the tools available now make cross-platform development a core strategic advantage.
Examples
- A social commerce startup launches features simultaneously on both platforms.
- Rapid A/B testing of UI changes across devices without doubling effort.
6. Biometric Everything
Passwords are becoming obsolete. The rise of passkeys and biometric logins is changing how users interact with apps. Face recognition, fingerprints, and secure hardware tokens are replacing traditional authentication, making sign-in frictionless and more secure.
For mobile apps in finance, e-commerce, healthcare, or any user-sensitive domain, seamless biometric integration is no longer optional. Users expect fast, secure access, and apps that do not provide it risk higher abandonment rates.
Example:
- A finance app that allows account access with a single fingerprint scan, removing multi-step login frustration.
7. Voice-First Interfaces
Mobile apps designed for voice-first interactions are gaining relevance as screenless experiences become more common in smart devices, cars, wearables, and AR environments.
Voice interfaces allow users to accomplish tasks without touching a screen, and they require new design thinking focused on natural language processing, contextual understanding, and user intent.
In 2026, apps that embrace voice-first design can engage users in ways that traditional screen-based interfaces cannot, providing accessibility, convenience, and a unique competitive edge.
Example:
- A navigation app that gives turn-by-turn directions and responds to spoken commands in real time.
8. Adaptive and Context-Aware UIs
User interfaces in 2026 are expected to be adaptive and context-aware, responding dynamically to device type, user behavior, and environmental conditions. For example, an app can switch layouts based on whether it is used on a wearable, tablet, or smartphone, or adjust notifications depending on location and activity. Adaptive UIs improve usability, reduce cognitive load, and increase engagement by delivering the right experience at the right time.
Examples:
- A messaging app that condenses the interface on smartwatches but shows full features on tablets.
- A news app that reduces push notifications during focus hours.
9. Sustainable and Efficient Apps
Energy efficiency and sustainability are becoming part of user expectations. Apps that consume less battery, optimize cloud usage, and reduce data transfer are favored by environmentally conscious users (of which there is a growing majority).
In 2026, sustainable app development is not just a marketing point. It directly affects user retention, app performance, and brand perception.
Example:
- A ride-sharing app that calculates routes and processes payments with minimal server calls, saving battery and data.
10. Embedded AR and Mixed Reality
Augmented reality and mixed reality are moving from novelty to functional utility in mobile apps. Retail, education, navigation, and healthcare apps increasingly integrate AR layers to provide real-time insights, interactive tutorials, and immersive experiences. In 2026, AR is no longer an optional add-on but a practical tool for engagement, decision-making, and differentiation in competitive categories.
Examples:
- Retail apps allowing virtual product try-ons.
- Educational apps overlaying 3D models for hands-on learning.
- Healthcare apps guiding rehabilitation exercises with AR instructions.
Conclusion
Trends alone do not create value. Each of the top mobile app development trends for 2026 comes with opportunities and challenges. Startups must focus on identifying which trends deliver measurable growth, meaningful engagement, and sustainable scalability. Filter the hype from the practical, and invest in the right technologies at the right time, so your apps not only survive in 2026 but thrive.


